Industrial development after World War II: costs and benefits
|
|
Industry |
Society
|
|
1950 – 1970 |
The III stage of the chemical industry. Period characterized in economic field by dominance of large oil multinationals (Seven Majors) Most attention centred on prevention of disasters in factories (fires, leaks) where automation is limited and risk of human error high. Catastrophic explosions of ammonium nitrate:
|
Industrial development brings increased well-being, thanks to job creation and availability of wide range of products which make daily life easier (nutrition, energy, home, health, etc). Better quality of life and life expectancy. Historical
records:
|
 |
Fig. 1: A picture of the ammonium nitrate explosion in the BASF chemical plant, Oppau (1921). |
|
|
Industry
|
Society
|
|
1970 – 1990 |
The IV stage of the chemical industry. First oil scare (1973) following Kippur Arab-Israeli war. Following introduction of first environmental legislation, start of industrial policies regarding pollution. |
Emotional environmentalism begins: anxiety about increasing pressure of technology on environment and health. Historical records:
|
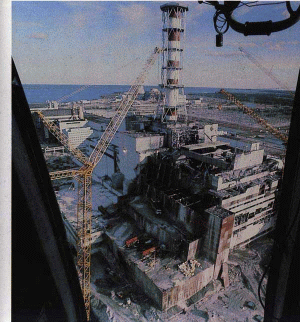 |
Fig. 2: Reactor n. 4 in Chernobyl after the explosion due to overheated steam and burning of graphite bars (April 26, 1986). 30 people died immediately. 135,000 people were evacuated in the surrounding 40-km radius because of the high radiation levels. |
|
|
Industry
|
Society
|
|
1990 - 2000
|
In western society, industry faces the "Total Quality" revolution. This includes:
In emerging countries with a high rate of development (India, Far East), little attention paid to environmental issues. |
Agenda 21, the Rio declaration on the environment and its development. (Rio de Janeiro, 1992). Kyoto protocol – United Nations convention on climate change (1997). Increased consumer pressure for quality in goods and services.
Sustainability The great
dichotomy: |
2000 -
|
Green chemistry |
World Summit on Sustainable Development (Johannesburg, South Africa, 2002). 16 Febbraio 2005 - The Kyoto Protocol comes into force, following its ratification by Russia. Terrorism (Twin Towers). Preventive war and reduced UN authority. Collective
emotional behaviour as result of economic crisis (Europe), globalization,
international terrorism and lack of a universally accepted global guide to
dictate new rules for sustainable
development Less importance given to environmental issues in media and public opinion.
|