Environmental chemistry
Environmental
chemistry![]() has been defined as the study of the
sources, reactions, transport, effects and fate
of chemical species in the environment, taken to mean water, air and soil and
living organisms.
has been defined as the study of the
sources, reactions, transport, effects and fate
of chemical species in the environment, taken to mean water, air and soil and
living organisms.
Environmental chemistry investigates at different levels (depending on the
problem) the state of health of the environment, from microhabitats to more
complex
ecosystems![]() to global compartments. This
state of health, in turn, reflects the consequences of past behaviour.
Environmental chemistry identifies and measures natural and manmade chemical
species and tries to understand the fate (mobility, residence time,
transformations) and effects of these on the environment. Analytical
chemistry is at the basis of any environmental research, but,
once the intended use of analytical data (site
characterization, monitoring of compliance with regulations, determination of
the degree of contamination, toxicological risk assessment, personnel
monitoring, remediation studies) has been established, the essential tasks for
the environmental chemist are: preparing sampling methods which meet the
intended aim, selecting appropriate analytical methods, interpreting data and
ensuring data
validation
to global compartments. This
state of health, in turn, reflects the consequences of past behaviour.
Environmental chemistry identifies and measures natural and manmade chemical
species and tries to understand the fate (mobility, residence time,
transformations) and effects of these on the environment. Analytical
chemistry is at the basis of any environmental research, but,
once the intended use of analytical data (site
characterization, monitoring of compliance with regulations, determination of
the degree of contamination, toxicological risk assessment, personnel
monitoring, remediation studies) has been established, the essential tasks for
the environmental chemist are: preparing sampling methods which meet the
intended aim, selecting appropriate analytical methods, interpreting data and
ensuring data
validation![]() for the purposes of legal defensibility.
for the purposes of legal defensibility.
The broad area of
environmental chemistry encompasses analytical chemistry, organic and inorganic
chemistry, radiation chemistry, chemical engineering, soil chemistry, chemical
toxicology and statistics. A challenge and a need for the environmental chemist is represented by team work,
working alongside all the users of
environmental data (ecologists, biologists, geologists, hydrogeologists,
toxicologists, and environmental engineers), because only through such an
interdisciplinary approach can we fully understand an environmental problem.
|
|
|
|
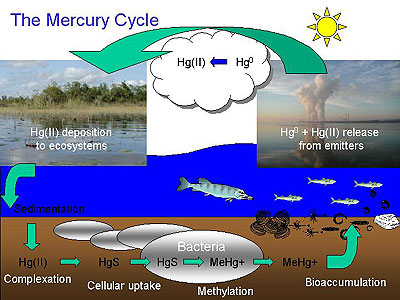
Fig. 1:
The
biogeochemical cycle (Credit: Academy of Natural Sciences - Estuarine Research Center) |
|
When we
discover in an ecosystem elements critical for the health and survival of the
organisms which live in it, it is likely that this is due to
polluting![]() chemical
substances. The relative study of environmental chemistry would consist of the
following steps:
chemical
substances. The relative study of environmental chemistry would consist of the
following steps:
- Planning an appropriate sampling and data collection strategy.
- Identifying the nature of the pollution (qualitative analysis).
- Identifying the extent (aerial study) and the level of pollution (quantitative survey).
- Tracking the source of the pollution: isolated incident or long-standing emission from a point-source, etc.
- Evaluating environmental mobility: how a substance can split and be transferred to the various environmental compartments (atmosphere, water, soil and sediment, living organisms).
- Assessing the most important transformations of the substance in the environment (hydrolysis, photolysis, oxidation, biodegradation) and the resultant average residence time in the various compartments.
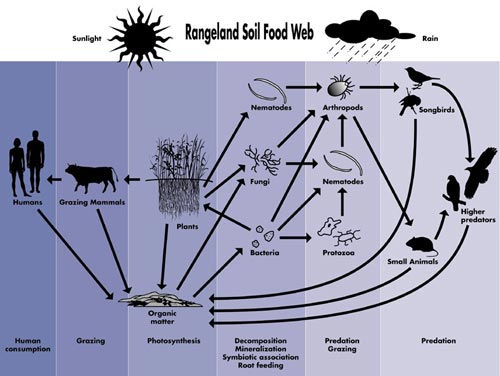 |
| Fig. 2:
A typical
food web (Credit: Soil Biological Communities) |

Fig. 3: The first Nobel Prizes for Environmental Chemistry.
The
ozone![]() layer - the Achilles heel of the
biosphere.
layer - the Achilles heel of the
biosphere.